Mask Images
Masks allow you to exclude specific areas of images from processing, such as windows, water, sky, shadows, vegetation, or image noise—from.. They are especially useful when scanning objects from multiple angles or orientations, helping to improve reconstruction accuracy and consistency by removing unwanted image data. Using masks can help filter out unwanted geometry during reconstruction, making the resulting model cleaner and reducing the need for extensive post-processing with the filtering tools.
Masks offer a non-destructive way to exclude parts of images from processing. They can be provided either as separate grayscale images (e.g., PNG files) or embedded in the alpha channel of the original images (e.g., TIFF files). In a mask, white areas will be used in processing, while black areas are excluded. Although grayscale values up to 256 shades (or partial transparency) can be used, they are not recommended, as they may interfere with processing and produce inconsistent results.
Generate Masks
Mask images can be generated using the AI Masking tool even before alignment, or after model creation using the Masking from Mesh tool. Both options are available in the Mask Images dropdown menu, located in the Process section of the ALIGNMENT tab.
- AI Masking Automatically detects the background and isolates the object of interest in the image. This option is ideal for turntable captures or environments with minimal background features.
- Masking from Mesh Generates mask images based on the reconstructed mesh as seen from the cameras in the scene. Areas outside the mesh are unmasked and will be ignored in further processing.
Import Mask Images
Mask images must follow the same naming principles as image layers during import. The required naming convention depends on whether you are importing individual files or loading all mask images from a folder. This is not needed if the images were generated using the AI Masking or Masking from Mesh tool they are automatically added to the project.
Learn more about image layers and how the naming convention works.
Export Options
Once generated using the AI Masking or Masking from Mesh tool, masks can be exported from the same dropdown menu where these tools are located. The same export option can also be used to save masks that were manually imported.
Masks can also be generated and exported automatically using the Maps and Masks button, available in the Export section of the MESH & COLOR tab or under SCENE 3D/TOOLS. These masks are created from the mesh in the same way as the Masking from Mesh generates masks, but they are not added to the project. Instead, they are exported directly alongside the depth maps. Depth maps store distance information between the camera and the visible surface, helping define which parts of the inserted object are visible. Masks are saved as PNG files, and depth maps as EXR files.
In the Export Depth Maps and Masks dialog window, you can choose whether to export masks from mesh, depth maps, or both. For more information about the undistortion settings available in the dialog, see Undistorted Images.
Visualize Masks
To view a mask, open the desired image in the 2D view and go to the Image 2D/VIEW tab. In the Source section of the ribbon, set the Input Layer to Mask. If the selected image does not have a mask layer, the option will be disabled.
If the image displayed in the 2D view has multiple image layers assigned to it, you can switch between them using the TAB key on the keyboard.
Use Mask Images
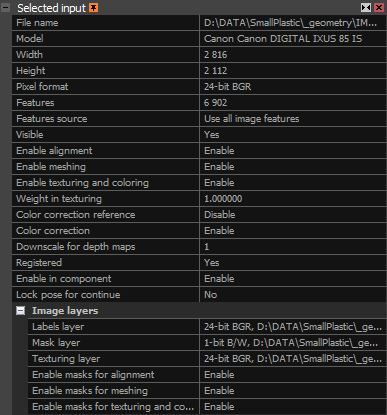
The Selected input panel appears when at least one input is selected. In the Image layers section, you can view all layers assigned to the selected image, including options for the mask layer if one is present. For the mask layer, you can set its availability during the alignment, meshing, or texturing process by changing the corresponding setting.